모던 자바스크립트 튜토리얼 part 1.8 프로토타입
- javascript
1. 내장 객체의 프로토타입
함수에는 기본적으로 prototype이라는 프로퍼티가 있으며, 이는 함수 자기 자신을 가리키는 constructor 프로퍼티 하나만 가지는 객체이다. 그리고 이는 함수가 new와 함께 쓰여 생성자 함수로 이용될 때 새로운 객체의 prototype이 된다.
내장 생성자 함수에도 prototype이 있다. 그럼 이는 어떻게 사용되는가?
1.1. Object.prototype
JS를 하는 사람이라면 다음과 같은 코드에서 나오는 [object Object]를 한번쯤 본 기억이 있다. 이는 어떻게 만들어지는 걸까?
let obj = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
};
alert(obj);
// [object Object]let obj = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
};
alert(obj);
// [object Object]프로토타입을 따로 지정하지 않은 모든 객체는 Object.prototype을 프로토타입으로 가진다. 즉 위의 obj 객체의 [[Prototype]]은 Object.prototype이다. 이때 Object.prototype의 프로토타입은 없다.
이 Object.prototype에는 toString과 같은 다양한 메소드가 구현되어 있다. 그래서 기본적으로 모든 객체는 toString을 사용할 수 있고 위의 obj도 마찬가지다. 그리고 그 결과물은 [object Object]이다.
let obj = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
};
console.log(obj.toString());
// [object Object]let obj = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
};
console.log(obj.toString());
// [object Object]왜 저렇게 변환되는지는 다른 글로 정리하고, 여기서는 객체들이 Object.prototype을 프로토타입으로 가지는 것만 알고 넘어가자.
또한 배열의 Array.prototype이나 함수의 Function.prototype과 같이 다른 내장 객체들의 프로토타입도 있는데 이들 모두 Object.prototype을 최상위 프로토타입으로 가진다.
또한 각 내장 객체 프로토타입들은 중복 메서드를 가질 수 있다. 예를 들어서 Object.prototype.toString과 Array.prototype.toString은 다른 동작을 한다.
let a = [1, 2, 3];
// [object Array]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(a));
// 1,2,3
console.log(Array.prototype.toString.call(a));let a = [1, 2, 3];
// [object Array]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(a));
// 1,2,3
console.log(Array.prototype.toString.call(a));console.dir을 이용해 객체 상속 관계도 확인 가능하다.
1.2. 프로토타입 조작하기
문자열, 숫자와 같은 원시값은 객체가 아닌데, 우리가 알다시피 이런 값들에도 메서드나 몇몇 프로퍼티를 사용할 수 있다. 이는 래퍼 객체를 통해 가능한 것이다.
그리고 명세서를 보면 이런 각 자료형에 해당하는 래퍼 객체 메서드를 prototype을 통해 구현한다. 예를 들어 String.prototype에는 문자열 전용 메서드가 구현되어 있다.
이를 이용하면 원시값의 프로토타입도 조작할 수 있다. 예를 들어 문자열의 프로토타입에 메서드를 추가할 수 있다.
String.prototype.show = function () {
alert(this);
};
let myName = "김성현";
myName.show();String.prototype.show = function () {
alert(this);
};
let myName = "김성현";
myName.show();그러나 이는 전역으로 영향을 미치기 때문에 추천할 만한 방식은 아니다. 폴리필을 만들 때나 사용할 만 하다.
2. 프로토타입 메서드와 __proto__없는 객체
__proto__를 통해서 객체의 프로토타입을 설정할 수 있다. 그러나 이는 낡은 방법이기 때문에 사용이 권장되지 않는다. 대신 다음과 같은 메서드들이 제공된다.
2.1. Object.create
Object.create(proto)는 객체를 생성하는데 사용된다. 이 메서드는 프로토타입을 인수로 받고 설명자를 선택적 인수로 받아서 빈 객체를 만든다.
이를 이용해서 상속을 구현할 수 있다. 단일 상속의 예시이다.
function Shape() {
this.x = 0;
this.y = 0;
}
Shape.prototype.move = function (x, y) {
this.x += x;
this.y += y;
console.log(`Shape moved to (${this.x}, ${this.y}).`);
};
function Rectangle() {
Shape.call(this);
}
/* Shape.prototype을 프로토타입으로 하는 Rectangle.prototype을 생성
그럼 Rectangle 인스턴스의 프로토타입은 Shape.prototype을 프로토타입으로갖는 어떤 객체이고
Shape.prototype은 constructor로 Shape 자신을 갖는 객체가 된다.
*/
Rectangle.prototype = Object.create(Shape.prototype);
Rectangle.prototype.constructor = Rectangle;
let rect = new Rectangle();
rect.move(1, 1); // Shape moved to (1, 1).
console.log(rect.__proto__.__proto__ === Shape.prototype); // truefunction Shape() {
this.x = 0;
this.y = 0;
}
Shape.prototype.move = function (x, y) {
this.x += x;
this.y += y;
console.log(`Shape moved to (${this.x}, ${this.y}).`);
};
function Rectangle() {
Shape.call(this);
}
/* Shape.prototype을 프로토타입으로 하는 Rectangle.prototype을 생성
그럼 Rectangle 인스턴스의 프로토타입은 Shape.prototype을 프로토타입으로갖는 어떤 객체이고
Shape.prototype은 constructor로 Shape 자신을 갖는 객체가 된다.
*/
Rectangle.prototype = Object.create(Shape.prototype);
Rectangle.prototype.constructor = Rectangle;
let rect = new Rectangle();
rect.move(1, 1); // Shape moved to (1, 1).
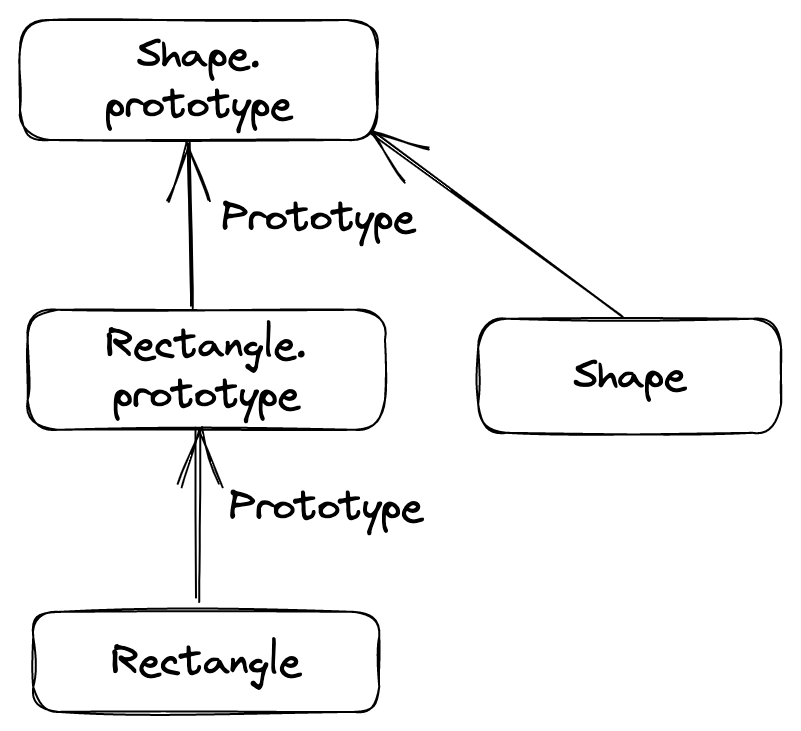
console.log(rect.__proto__.__proto__ === Shape.prototype); // true위의 예시 코드의 상속 구조를 다음과 같이 생각할 수 있다. 이 사이트로 그림을 그려보았다.
2번째 인수로는 설명자를 지정할 수 있는데 이는 Object.defineProperties의 두 번째 인수와 같은 역할을 한다. 이 말은 즉 writable, enumerable, configurable이 기본적으로 false로 설정되어 있다는 것도 있다.
let obj = Object.create(Object.prototype, {
foo: { value: "foo-1", writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true },
bar: { value: "bar-1", writable: true, configurable: true },
});
// bar의 enumerable 속성이 디폴트인 false이므로 for-in 루프에서 제외된다.
for (let key in obj) {
console.log(key, obj[key]); // foo foo-1
}let obj = Object.create(Object.prototype, {
foo: { value: "foo-1", writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true },
bar: { value: "bar-1", writable: true, configurable: true },
});
// bar의 enumerable 속성이 디폴트인 false이므로 for-in 루프에서 제외된다.
for (let key in obj) {
console.log(key, obj[key]); // foo foo-1
}또한 Object.create를 써서 효과적으로 프로퍼티 전부를 얕은 복사할 수 있다. 열거 가능/불가능 프로퍼티, getter, setter, 데이터 프로퍼티 등 모두가 복사된다.
// obj의 완벽한 복사본을 리턴
Object.create(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj), Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj));// obj의 완벽한 복사본을 리턴
Object.create(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj), Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj));2.2. Object.getPrototypeOf, Object.setPrototypeOf
Object.getPrototypeOf(obj)는 객체의 프로토타입을 반환한다. Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, proto)는 객체의 프로토타입을 설정한다.
2.3. 단순한 객체
객체는 키-값 쌍이 있는 연관 배열로 사용할 수 있다. 그런데 __proto__문자열은 키로 제대로 사용할 수 없다. __proto__는 객체의 프로토타입을 나타내는 내부 프로퍼티(표준은 아니지만 사실상 표준인)이고 객체 혹은 null이 되어야 하는 것이다.
물론 객체 대신 Map을 쓰면 된다. 하지만 객체에서도 이를 해결할 수 있다.
먼저 __proto__는 객체의 데이터 프로퍼티가 아니라 Object.prototype의 getter, setter로 설정된 접근자 프로퍼티이다. 즉 __proto__를 키로 사용하면 객체의 프로토타입인 Object.prototype의 접근자 프로퍼티에 접근하는 것이다.
이를 해결하기 위해서는 프로토타입이 없는 빈 객체를 만들면 된다. Object.create로 만들 수 있다. 그러면 __proto__에 접근할 때 Object.prototype을 검색할 수 없으므로 자유로워진(?) __proto__를 키로 사용할 수 있다.
let simpleObj = Object.create(null);
simpleObj.__proto__ = "hi";
console.log(simpleObj.__proto__);
// hilet simpleObj = Object.create(null);
simpleObj.__proto__ = "hi";
console.log(simpleObj.__proto__);
// hi이런 객체를 아주 단순한(very plain) 객체라고 부른다. 단 프로토타입이 없으므로 객체의 기본 메서드를 사용할 수 없다.
let simpleObj = Object.create(null);
simpleObj.__proto__ = "hi";
console.log(simpleObj.toString());
// toString이 없으므로 에러let simpleObj = Object.create(null);
simpleObj.__proto__ = "hi";
console.log(simpleObj.toString());
// toString이 없으므로 에러2.4. 객체 메서드
객체에는 Object.keys, Object.values와 같이 프로퍼티를 반환하는 다양한 메서드들이 있다. 그러나 이들은 객체가 직접 소유한 프로퍼티만 반환한다. 상속 프로퍼티는 제외된다.
let proto = {
foo: "hello",
};
let obj = {
bar: "world",
};
Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, proto);
console.log(obj.foo); // foo에 접근 가능. "hello"
console.log(Object.keys(obj));
// 프로토타입의 프로퍼티는 제외되어 ["bar"]만 있다.let proto = {
foo: "hello",
};
let obj = {
bar: "world",
};
Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, proto);
console.log(obj.foo); // foo에 접근 가능. "hello"
console.log(Object.keys(obj));
// 프로토타입의 프로퍼티는 제외되어 ["bar"]만 있다.참고
Object.create MDN문서 https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Object/create